FabricPath facts

Creator of STP, Radia Perlman, developed TRILL – Transparent Interconnect of Lots of Link to overcome the limitations of STP. Cisco enhanced the protocol and named it FabricPath.
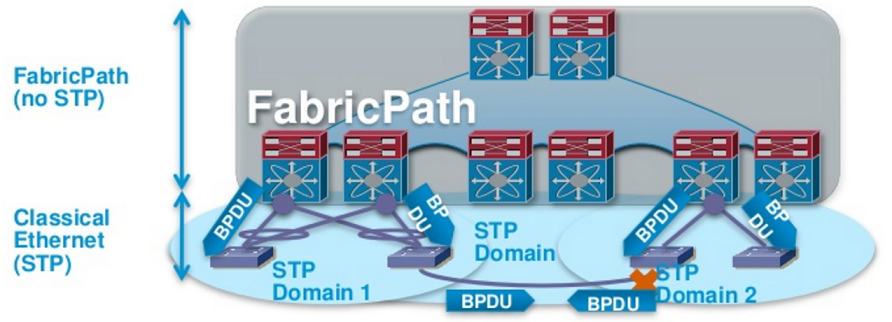
Limitation of STP – As the figure above clearly shows that STP allows only a single path to destination in a L2 domain and blocks the redundant path. Whereas Fabricpath enables all path, scalable upto 16 ECMP, which ensures the utilization of full available bandwidth.
Difference with vPC - vPC addresses the blocked link limitation, but is only scalable to two spine or core switch and still relies on STP for loop prevention. vPC+, an enhanced version of vPC can be used in conjunction with fabricpath.
A single switch – A cloud of fabricpath capable switches can also be connected to a traditional STP network, where the cloud is considered as one single switch. Ideally, the fabricpath cloud is configured as root bridge in the STP domain.
Link state protocol – Layer 3 routing intelligence brought to Layer 2. FabricPath uses ISIS routing protocol with FabricPath-specific extensions, like exchanging switch ID (SID) to determine reachability and path selection in the FabricPath domain.
Conversational learning of mac address – In a classical switched network all switches maintains table all MAC address of hosts in the network. This table, TCAM can grow larger as hosts increases. Fabricpath switch learns remote MAC addresses only if the remote device is having a bidirectional conversation with a locally connected device.